
Introduction to Powertrain
In this chapter we give a brief introduction to the power system of the electric tricycle.
If you don’t know anything about the powertrain of electric tricycles, then you will like this chapter.
In the following chapters we will introduce other parts of the electric tricycle power system.
But for now let’s briefly review the powertrain of an electric tricycle
Broadly speaking, the power system of an electric tricycle consists of a drive motor, a motor controller, a battery, a differential and wheels.
The motor controller receives output signals from the speed control lever and brake.
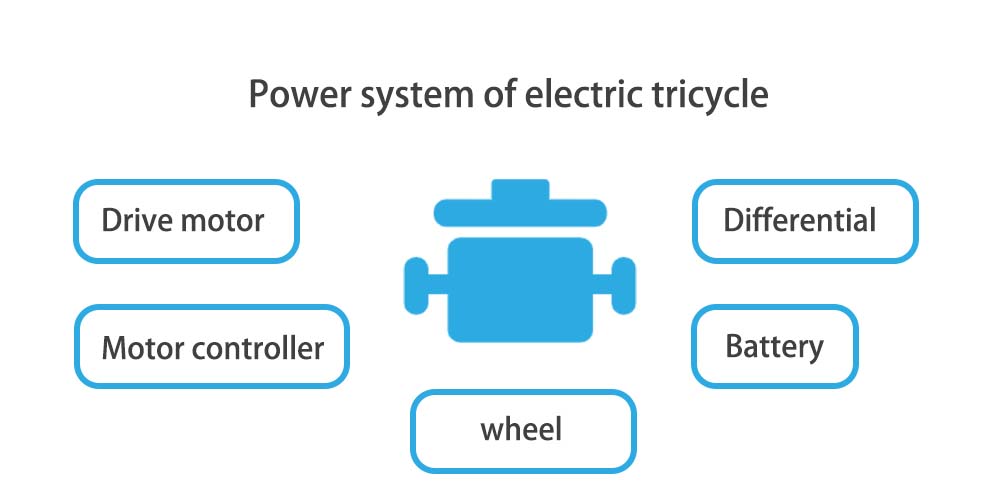
Different gears control the rotation of the drive motor, and drive the wheels through mechanical transmissions such as differentials and axle shafts. According to the type of controller and navigation motor, electric tricycle power system can be divided into permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) power system and brushless DC motor (BLDC) power system.
The power system of the electric tricycle is the link between the energy storage system and the wheels.
Its function is to convert the electrical energy output by the battery into mechanical energy, push the vehicle to overcome various rolling resistance, air resistance, acceleration resistance, climbing resistance, and convert kinetic energy during braking.
Converted into electrical energy and fed back to the energy storage system. Modern electric tricycles are different from traditional gasoline tricycles.
Their powertrains can eliminate the need for complex mechanical shifting structures and provide torque and speed characteristics for a wide range of vehicle speeds and significant load changes.
Drive motor
In this chapter, we are going to introduce the drive motor.
There are different types of drive motors.
Of course, the corresponding performance will be different. So let’s find out together.
The drive motor provides power, and the categories are relatively rich.
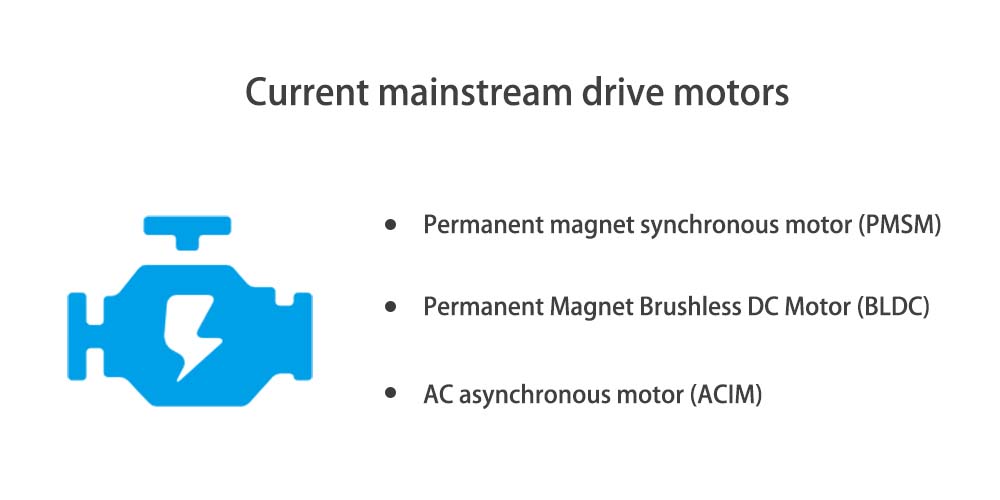
Nevertheless, currently in the electric tricycle industry, the current mainstream drive motors are permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), permanent magnet brushless DC motor (BLDC), and AC asynchronous motor (ACIM).
These motors have their characteristics in performance, structure, and control methods and are suitable for different electric tricycles and usage scenarios.
Due to the stator current, permanent magnet brushless DC motors (BLDC) have square or trapezoidal waves.
The air-gap flux density is usually designed as a square wave, or close to a square wave, so the rotor is generally made into a tile to maximize its output.
Motor Controller
The motor controller is the core control device used to control the starting, run, advancing, retreat, speed regulation, stop, and other electronic types of electric vehicle drive motor equipment.
It is an integral part of an electric tricycle.
Motor controllers also have different performance and characteristics depending on the model.
Now I will analyze it for you.
The motor control system of the electric vehicle tricycle should choose a suitable microprocessor system according to the complexity of its control algorithm.
The simpler one is to use the single-chip controller, the more complex one can use the DSP controller, and the recently-appeared special-purpose chip for a motor drive can meet the motor control requirements of some auxiliary systems.
The control circuit mainly includes the following parts: control chip and its drive system, AD sampling system, power module, drive system, hardware protection system, position detection system, bus support capacitor, etc.
The primary power circuit adopts a three-phase inverter full-bridge, and the primary power switching device is IG-BT.
In the state of high current and high-frequency switching, the stray inductance from the electrolytic capacitor to the power switch module has a significant influence on the energy consumption of the power circuit and the peak voltage on the module.
Therefore, a laminated busbar substrate is used to reduce the stray inductance of the course.
It should be as small as possible to adapt to the characteristics of the control system’s low voltage and high current operation.
At present, the controller of an electric bicycle, whether it is brushed or brushless, generally adopts the pulse width modulation (PWM) method.
The controller must have a PWM generator circuit, power supply circuit, power device, drive circuit, control component (turn handle, brake handle, motor Hall, etc.), signal acquisition and processing circuit, and overcurrent and Undervoltage protection circuits.
Most brushed and brushless DC motors use the PWM control method of pulse width modulation to control the speed, but the difference in selecting driving circuits, integrated circuits, switching circuit power transistors, and some related functions.
Differences in components and circuits make up the difference in controller performance.
The controller is divided into two types in the structure; we call it a different type and integral type.
The design quality and characteristics of the electric vehicle motor controller, the function of the microprocessor used, the power switching device circuit and the layout of peripheral devices, etc., are directly related to the performance and operating status of the entire vehicle, and also affect the performance and efficiency of the controller itself.
Controllers of different quality, used in the exact vehicle and equipped with the same set of batteries in the same charge and discharge state, sometimes show significant differences in driving ability.
Differential mechanism
The differential plays a pivotal role in the powertrain of an electric tricycle So how does it work If you want to know, please read this chapter with me.
A differential is a structure that enables the left and right drive wheels to rotate at different speeds. It is mainly composed of left and right side shaft gears, two planetary gears, and a gear carrier.
Its function is to make the left and right wheels roll at different speeds when the car turns or drives on uneven roads, that is, to ensure that the driving wheels on both sides perform the pure rolling motion.
Ordinary differentials include planetary gears, carriers (differential housings), side gears, and other components.
The drive motor’s power enters the differential through the driveshaft and directly drives the planetary carrier.
Then the planetary gear drives the left and suitable half shafts to drive the left and right wheels.
When the electric tricycle runs straight, the rotational speed of the left and right wheels and the planetary carrier are equal and in a balanced state.
But the balance of the three is destroyed when cornering, resulting in a drop in wheel speed—an increase in the rotational speed of the inner and outer wheels.
Batteries
“Electric” tricycles, as the name suggests, require electricity. So, where does electricity come from? I think you should be very curious to know.
Then keep reading.
The battery in an electric tricycle is a device that directly converts chemical energy into electrical energy.

It is a rechargeable battery designed to be charged through a reversible chemical reaction.
The battery uses external electrical energy to regenerate the internal active material when charging, stores the electrical energy as chemical energy, and converts it into electrical energy for output when it needs to be discharged.
The batteries of electric tricycles can usually be divided into lead-acid batteries and lithium batteries.
Lead-acid batteries are generally used in electric cargo tricycles and full-cover passenger tricycles, and lithium batteries are partly used in emerging recreational tricycles.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoy this 2022 updated guide to electric tricycle powertrains.
Now I want to hear from you: Is this your understanding of the power system of an electric tricycle?
Let me know by leaving a quick comment below now.



